Wind Turbine Transformer Colour

It is preferable to house wind turbine transformers within the turbine towers to minimise the number of elements and visual complexity of a wind farm. However, where transformers are housed separately near the turbine bases, the colour of the housing requires careful consideration. This should be site specific, relating to the surrounding land cover, but not the wind turbines, as transformers are rarely viewed against the skyline. This reduces their visibility and ensures that they are seenas a separate element to the turbine. They are less likely to detract from the simplicity of the turbine’s form if well located and coloured. Browns, khakis and ‘earth’ colours are generally the most successful colour choices for transformers, with greens often appearing too bright.
In some locations it may be necessary to light wind turbines for reasons of civil or military aviation safety or, for offshore wind farms, marine safety. Such lighting, typically at the top of the tower of the wind turbine, may appear prominent in night views and be incongruous in predominantly un-lit rural areas. Where lighting is necessary, it should be designed to minimise landscape and visual impacts whilst satisfying health and safety or navigation requirements. This may, for example, be achieved by incorporating shields so that the lights can only be seen from above.Developers should always refer to the NATS, CAA and MoD for current requirements. Lighting is predicted to become more widespread as sites are explored within flight pathsb and as larger turbines are considered. Current experience suggests that the main landscape and visual effects are likely to include:
–lighting visible over considerable distance. The Beatrice offshore turbines, off the Caithness coast are visible in clear conditions at distances of over 20 kilometres;
–movement of turbine blades will create different effects depending on where the viewer is, in relation to the wind farm. If the turbine blades pass in front of the light, a flashing effect as they cut across the light is created. If the blades pass behind the light, the are is a striped effect as the light runs up the passing blades. In both cases the seeffects draw the eye to the turbines;
–there may be situations where constantly flashing lights are required, especially offshore;
–in certain light conditions, lighting may appear to float above the ground even where the turbines themselves are not visible.
Labels
wind power generatorwind turbine generatorwind power generationwind turbine pricewind power plantwind turbine modelmodel wind turbinesiemens wind turbineswind power turbineswind power plant pptFarming Principle: Deep Soil Preparation
Looking at GB as a three-legged stool, deep soil preparation is one of the legs. Deep soil preparation builds soil and soil structure by loosening the soil to a depth of 24 inches (60 cm). Ideal soil structure has both pore space for air and water to move freely and soil particles that hold together nicely.
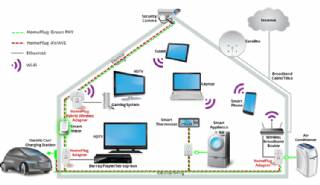
Smart Home Ecosystem - Smart Home Automation - Smart Home Security - Smart Home Technology
The outer-most level corresponds to the individual devices and sensors that consumers interact with. Several candidates are vying for the role of a leader introducing smart home services to the mass market.
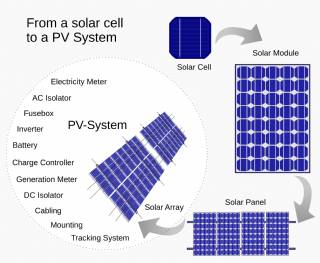
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Modules - Solar Electric System Design - Solar Power
The heart of a photovoltaic system is the solar module. Many photovoltaic cells are wired together by the manufacturer to produce a solar module. When installed at a site, solar modules are wired together in series to form strings. Strings of modules are connected in parallel to form an array.
Solar Energy Systems - Array Mounting Racks - Solar Ray - Solar Panel - PV Racks and Mounts
Arrays are most commonly mounted on roofs or on steel poles set in concrete. In certain applications, they may be mounted at ground level or on building walls. Solar modules can also be mounted to serve as part or all of a shade structure such as a patio cover. On roof-mounted systems, the PV array is typically mounted on fixed racks, parallel to t

Solar Energy Systems - Grounding Equipment
Grounding equipment provides a well-defined, low-resistance path from your system to the ground to protect your system from current surges from lightning strikes or equipment malfunctions. Grounding also stabilizes voltages and provides a common reference point. The grounding harness is usually located on the roof.
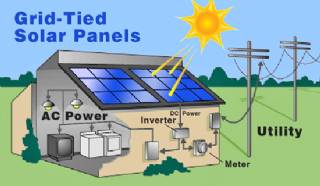
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Inverter - Solar Panel Inverter
Most grid-connected inverters can be installed outdoors, while most off-grid inverters are not weatherproof. There are essentially two types of grid-interactive inverters: those designed for use with batteries and those designed for a system without batteries.
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Disconnects
Automatic and manual safety disconnects protect the wiring and components from power surges and other equipment malfunctions. They also ensure the system can be safely shut down and system components can be removed for maintenance and repair.

Solar Energy Systems - Solar Battery Bank
Batteries store direct current electrical energy for later use. This energy storage comes at a cost, however, since batteries reduce the efficiency and output of the PV system, typically by about 10 percent for lead-acid batteries. Batteries also increase the complexity and cost of the system.
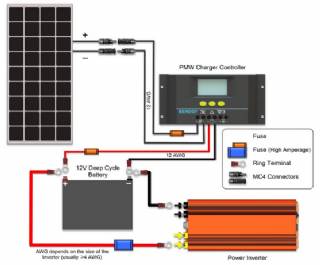
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Charge Controller
A charge controller, sometimes referred to as a photovoltaic controller or battery charger, is only necessary in systems with battery back-up. The primary function of a charge controller is to prevent overcharging of the batteries. Most also include a lowvoltage disconnect that prevents over-discharging batteries. In addition, charge controllers pr
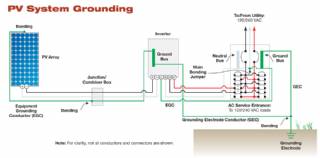
Solar Energy Systems - The NEC and PV Systems
Solar PV systems must be installed in accordance with Article 690 of the National Electric Code, which specifically deals with PV systems, as well as several other articles of the NEC that pertain to electrical systems in general. When there is a conflict between NEC 690 and any other article, NEC 690 takes precedence due to the unique nature of PV