Solar Energy Systems - Solar Charge Controller
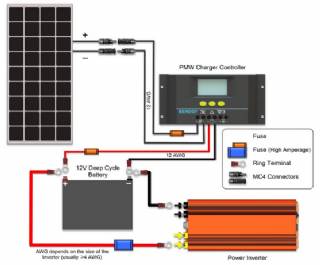
A charge controller, sometimes referred to as a photovoltaic controller or battery charger, is only necessary in systems with battery back-up. The primary function of a charge controller is to prevent overcharging of the batteries. Most also include a lowvoltage disconnect that prevents over-discharging batteries. In addition, charge controllers prevent charge from draining back to solar modules at night. Some modern charge controllers incorporate maximum power point tracking, which optimizes the PV array’s output, increasing the energy it produces.
Types of Charge Controllers – There are essentially two types of controllers: shunt and series. A shunt controller bypasses current around fully charged batteries and through a power transistor or resistance heater where excess power is converted into heat. Shunt controllers are simple and inexpensive, but are only designed for very small systems. Series controllers stop the flow of current by opening the circuit between the battery and the PV array. Series controllers may be single-stage or pulse type. Single-stage controllers are small and inexpensive and have a greater load-handling capacity than shunt-type controllers. Pulse controllers and a type of shunt controller referred to as a multi-stage controller (e.g., three-stage controller) have routines that optimize battery charging rates to extend battery life.
Most charge controllers are now three-stage controllers. These chargers have dramatically improved battery life.
Selection – Charge controllers are selected based on:
• PV array voltage – The controller’s DC voltage input must match the nominal voltage of the solar array.
• PV array current – The controller must be sized to handle the maximum current produced by the PV array.
Interaction with Inverter – Since the majority of charge controllers have been installed in off-grid systems, their default settings may not be appropriate for a grid-connected system. The charge controller must be set up such that it does not interfere with the proper operation of the inverter. In particular, the controller must be set up such that charging the batteries from the PV array takes precedence over charging from the grid.
Interaction with Batteries – The charge controller must be selected to deliver the charging current appropriate for the type of batteries used in the system. For example, on a 12V system, flooded lead-acid batteries have a voltage of 14.6V to 15.0V when fully charged, while sealed lead-acid batteries are fully charged at 14.1 V. Refer to the battery manufacturer for the charging requirements of particular batteries.
Labels
solarsolar charge controllerchargeoff gridcharge controllerssolar powercontrollerpwm charge controllermppt charge controllergoing solaranselfreviewlithiumsolarpennysolar pennyhow to size charge controlleroff grid powergo solarli310go off gridmaximum power point trackinglow voltage disconnectamazonmohooload controllersolar load controlsolar load controllerload controlwhat is a solar charge controllerwhat is a charge cFarming Principle: Deep Soil Preparation
Looking at GB as a three-legged stool, deep soil preparation is one of the legs. Deep soil preparation builds soil and soil structure by loosening the soil to a depth of 24 inches (60 cm). Ideal soil structure has both pore space for air and water to move freely and soil particles that hold together nicely.
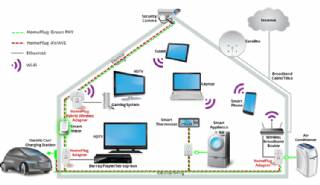
Smart Home Ecosystem - Smart Home Automation - Smart Home Security - Smart Home Technology
The outer-most level corresponds to the individual devices and sensors that consumers interact with. Several candidates are vying for the role of a leader introducing smart home services to the mass market.
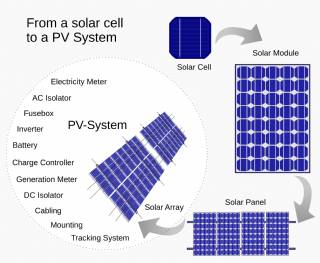
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Modules - Solar Electric System Design - Solar Power
The heart of a photovoltaic system is the solar module. Many photovoltaic cells are wired together by the manufacturer to produce a solar module. When installed at a site, solar modules are wired together in series to form strings. Strings of modules are connected in parallel to form an array.
Solar Energy Systems - Array Mounting Racks - Solar Ray - Solar Panel - PV Racks and Mounts
Arrays are most commonly mounted on roofs or on steel poles set in concrete. In certain applications, they may be mounted at ground level or on building walls. Solar modules can also be mounted to serve as part or all of a shade structure such as a patio cover. On roof-mounted systems, the PV array is typically mounted on fixed racks, parallel to t

Solar Energy Systems - Grounding Equipment
Grounding equipment provides a well-defined, low-resistance path from your system to the ground to protect your system from current surges from lightning strikes or equipment malfunctions. Grounding also stabilizes voltages and provides a common reference point. The grounding harness is usually located on the roof.
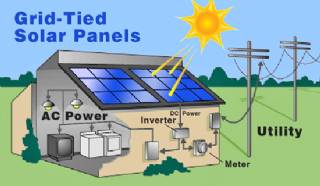
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Inverter - Solar Panel Inverter
Most grid-connected inverters can be installed outdoors, while most off-grid inverters are not weatherproof. There are essentially two types of grid-interactive inverters: those designed for use with batteries and those designed for a system without batteries.
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Disconnects
Automatic and manual safety disconnects protect the wiring and components from power surges and other equipment malfunctions. They also ensure the system can be safely shut down and system components can be removed for maintenance and repair.

Solar Energy Systems - Solar Battery Bank
Batteries store direct current electrical energy for later use. This energy storage comes at a cost, however, since batteries reduce the efficiency and output of the PV system, typically by about 10 percent for lead-acid batteries. Batteries also increase the complexity and cost of the system.
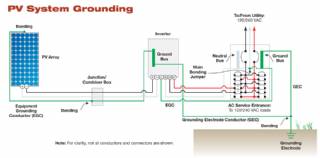
Solar Energy Systems - The NEC and PV Systems
Solar PV systems must be installed in accordance with Article 690 of the National Electric Code, which specifically deals with PV systems, as well as several other articles of the NEC that pertain to electrical systems in general. When there is a conflict between NEC 690 and any other article, NEC 690 takes precedence due to the unique nature of PV
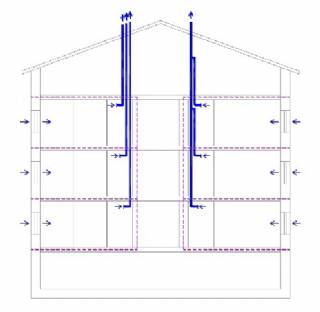
Ventilation Systems - Natural Ventilation
The bigger the both factors are the more intensive is the air change in rooms. This means that in colder weather conditions the rooms and the building is often over-ventilated and in warmer and windless weather, there is a lack of fresh air. As both of these factors are directly dependent on the external climate, the system is considered to be a no