Solar Energy Systems - Solar Disconnects
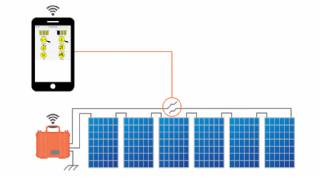
Automatic and manual safety disconnects protect the wiring and components from power surges and other equipment malfunctions. They also ensure the system can be safely shut down and system components can be removed for maintenance and repair. For gridconnected systems, safety disconnects ensure that the generating equipment is isolated from the grid, which is important for the safety of utility personnel. In general, a disconnect is needed for each source of power or energy storage device in the system.
For each of the functions listed below, it is not always necessary to provide a separate disconnect. For example, if an inverter is located outdoors, a single DC disconnect can serve the function of both the array DC disconnect and the inverter DC disconnect. Before omitting a separate disconnect, however, consider if this will ever result in an unsafe condition when performing maintenance on any component. Also consider the convenience of the disconnect’s location. An inconveniently located disconnect may lead to the tendency to leave the power on during maintenance, resulting in a safety hazard.
Array DC Disconnect – The array DC disconnect, also called the PV disconnect, is used to safely interrupt the flow of electricity from the PV array for maintenance or troubleshooting. The array DC disconnect may also have integrated circuit breakers or fuses to protect against power surges.
Inverter DC Disconnect – Along with the inverter AC disconnect, the inverter DC disconnect is used to safely disconnect the inverter from the rest of the system. In many cases, the inverter DC disconnect will also serve as the array DC disconnect.
Inverter AC Disconnect – The inverter AC disconnect disconnects the PV system from both the building’s electrical wiring and the grid. Frequently, the AC disconnect is installed inside the building’s main electrical panel. However, if the inverter is not located near the electrical panel, an additional AC disconnect should be installed near the inverter.
Exterior AC Disconnect – Utilities commonly require an exterior AC disconnect that is lockable, has visible blades and is mounted next to the utility meter so that it is accessible to utility personnel. An AC disconnect located inside the electrical panel or integral to the inverter would not satisfy these requirements. One alternative that is as acceptable to some utilities as an accessible AC disconnect is the removal of the meter itself, but this is not the norm. Prior to purchasing equipment, consult the electric utility to determine their requirements for interconnection.
Battery DC Disconnect – In a battery-based system, the battery DC disconnect is used to safely disconnect the battery bank from the rest of the system.
Labels
discosolarelectricwarmingsolar energy (industry)60 amp disconnect boxsolar installationsolar energysolar panelssolar kitssolar installation murrietaalternativesolar gticleanenvironmentelectricitygreenchangeclimateglobalsolar power disconnect boxesgrid tie invertersolar grid tie inverterssolar panel kitssolar gti systemsolar (album)solar powersolar panelpanelssolar power grid tie inverterconstructionearthshipFarming Principle: Deep Soil Preparation
Looking at GB as a three-legged stool, deep soil preparation is one of the legs. Deep soil preparation builds soil and soil structure by loosening the soil to a depth of 24 inches (60 cm). Ideal soil structure has both pore space for air and water to move freely and soil particles that hold together nicely.
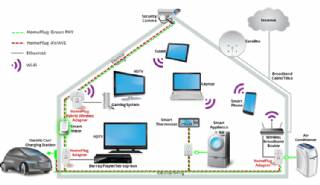
Smart Home Ecosystem - Smart Home Automation - Smart Home Security - Smart Home Technology
The outer-most level corresponds to the individual devices and sensors that consumers interact with. Several candidates are vying for the role of a leader introducing smart home services to the mass market.
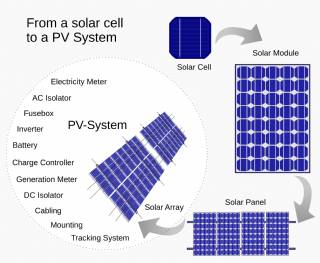
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Modules - Solar Electric System Design - Solar Power
The heart of a photovoltaic system is the solar module. Many photovoltaic cells are wired together by the manufacturer to produce a solar module. When installed at a site, solar modules are wired together in series to form strings. Strings of modules are connected in parallel to form an array.
Solar Energy Systems - Array Mounting Racks - Solar Ray - Solar Panel - PV Racks and Mounts
Arrays are most commonly mounted on roofs or on steel poles set in concrete. In certain applications, they may be mounted at ground level or on building walls. Solar modules can also be mounted to serve as part or all of a shade structure such as a patio cover. On roof-mounted systems, the PV array is typically mounted on fixed racks, parallel to t

Solar Energy Systems - Grounding Equipment
Grounding equipment provides a well-defined, low-resistance path from your system to the ground to protect your system from current surges from lightning strikes or equipment malfunctions. Grounding also stabilizes voltages and provides a common reference point. The grounding harness is usually located on the roof.
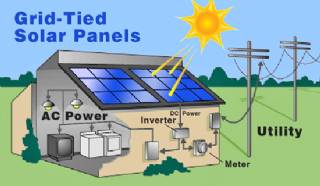
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Inverter - Solar Panel Inverter
Most grid-connected inverters can be installed outdoors, while most off-grid inverters are not weatherproof. There are essentially two types of grid-interactive inverters: those designed for use with batteries and those designed for a system without batteries.

Solar Energy Systems - Solar Battery Bank
Batteries store direct current electrical energy for later use. This energy storage comes at a cost, however, since batteries reduce the efficiency and output of the PV system, typically by about 10 percent for lead-acid batteries. Batteries also increase the complexity and cost of the system.
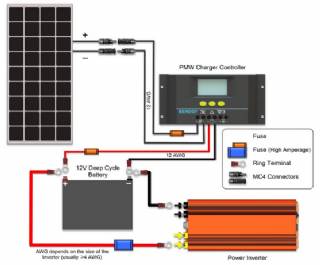
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Charge Controller
A charge controller, sometimes referred to as a photovoltaic controller or battery charger, is only necessary in systems with battery back-up. The primary function of a charge controller is to prevent overcharging of the batteries. Most also include a lowvoltage disconnect that prevents over-discharging batteries. In addition, charge controllers pr
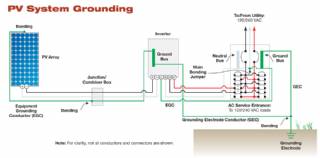
Solar Energy Systems - The NEC and PV Systems
Solar PV systems must be installed in accordance with Article 690 of the National Electric Code, which specifically deals with PV systems, as well as several other articles of the NEC that pertain to electrical systems in general. When there is a conflict between NEC 690 and any other article, NEC 690 takes precedence due to the unique nature of PV
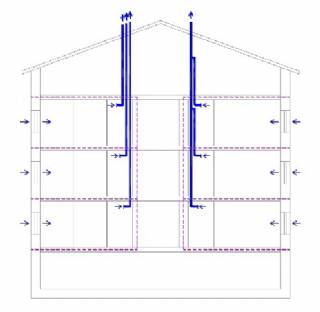
Ventilation Systems - Natural Ventilation
The bigger the both factors are the more intensive is the air change in rooms. This means that in colder weather conditions the rooms and the building is often over-ventilated and in warmer and windless weather, there is a lack of fresh air. As both of these factors are directly dependent on the external climate, the system is considered to be a no