Wind Turbine Form And Design

A wind turbine comprises a tower that supports a nacelle which contains the electric generator and to which the turbine blades attach via a hub. Further guidance on wind turbines isavailable in the Scottish Government Planning Advice Note “Onshore wind Turbines”.
The landscape and visual impacts of a wind turbine vary not only with its size, but also with the make and model of the turbine proposed. Turbines of the same height may have varying appearances due to their different design and technical characteristics. There is an incre asingly varied selection of turbine designs now available, especially in the lower height ranges. For further detail see our guidance on the siting and design of small scale turbines.
It can be difficult for wind turbine developers to specify the actual model of turbine to be used because market availability, costs, and turbine technology may change during the period between submitting an application and actual construction. However, they will usually have a shortlist of preferred models for consideration and applications should include details of these. The LVIA and EIA should assess, as far as is possible, impacts of the model within the shortlist that represents the ‘worst case scenario’.
Turbine properties which are important when choosing the most appropriate model for a site include:
– the proportion of blade length to tower height;
–overall height to blade tip, colour and individual design
–the turbine’s dynamic impact, resulting from rotation of its blades (larger, slow moving blades will have a very different impact from shorter, faster moving blades which may give the impression of increased clutter); and
–consistency with other existing and consented turbines in the vicinity.
Labels
wind turbine designhow does wind energy workwind turbine bladeswind turbine blade designvertical wind turbinesmall wind turbinevertical axis wind turbinemost efficient wind turbineFarming Principle: Deep Soil Preparation
Looking at GB as a three-legged stool, deep soil preparation is one of the legs. Deep soil preparation builds soil and soil structure by loosening the soil to a depth of 24 inches (60 cm). Ideal soil structure has both pore space for air and water to move freely and soil particles that hold together nicely.
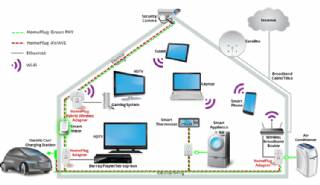
Smart Home Ecosystem - Smart Home Automation - Smart Home Security - Smart Home Technology
The outer-most level corresponds to the individual devices and sensors that consumers interact with. Several candidates are vying for the role of a leader introducing smart home services to the mass market.
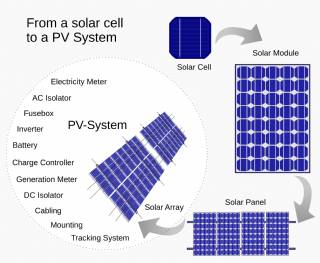
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Modules - Solar Electric System Design - Solar Power
The heart of a photovoltaic system is the solar module. Many photovoltaic cells are wired together by the manufacturer to produce a solar module. When installed at a site, solar modules are wired together in series to form strings. Strings of modules are connected in parallel to form an array.
Solar Energy Systems - Array Mounting Racks - Solar Ray - Solar Panel - PV Racks and Mounts
Arrays are most commonly mounted on roofs or on steel poles set in concrete. In certain applications, they may be mounted at ground level or on building walls. Solar modules can also be mounted to serve as part or all of a shade structure such as a patio cover. On roof-mounted systems, the PV array is typically mounted on fixed racks, parallel to t

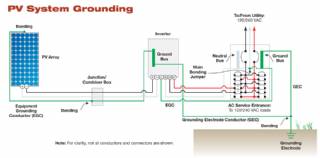
Solar Energy Systems - Grounding Equipment
Grounding equipment provides a well-defined, low-resistance path from your system to the ground to protect your system from current surges from lightning strikes or equipment malfunctions. Grounding also stabilizes voltages and provides a common reference point. The grounding harness is usually located on the roof.
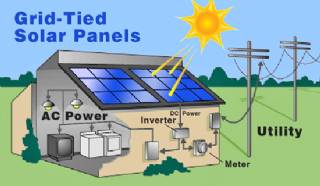
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Inverter - Solar Panel Inverter
Most grid-connected inverters can be installed outdoors, while most off-grid inverters are not weatherproof. There are essentially two types of grid-interactive inverters: those designed for use with batteries and those designed for a system without batteries.
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Disconnects
Automatic and manual safety disconnects protect the wiring and components from power surges and other equipment malfunctions. They also ensure the system can be safely shut down and system components can be removed for maintenance and repair.

Solar Energy Systems - Solar Battery Bank
Batteries store direct current electrical energy for later use. This energy storage comes at a cost, however, since batteries reduce the efficiency and output of the PV system, typically by about 10 percent for lead-acid batteries. Batteries also increase the complexity and cost of the system.
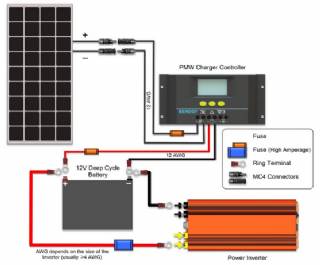
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Charge Controller
A charge controller, sometimes referred to as a photovoltaic controller or battery charger, is only necessary in systems with battery back-up. The primary function of a charge controller is to prevent overcharging of the batteries. Most also include a lowvoltage disconnect that prevents over-discharging batteries. In addition, charge controllers pr
Solar Energy Systems - The NEC and PV Systems
Solar PV systems must be installed in accordance with Article 690 of the National Electric Code, which specifically deals with PV systems, as well as several other articles of the NEC that pertain to electrical systems in general. When there is a conflict between NEC 690 and any other article, NEC 690 takes precedence due to the unique nature of PV