Planning Constraints For Wind Turbines

There is a number of planning related issues that may make it difficult for you to install a turbine on your site and it would be wise to ensure that you are not going to fall foul of any of these before proceeding.
o Military installations.
Avoid these installations, especially if it is an air force base or communication centres.
o Proximity to built-up area.
When housing estates are concerned, ideally consider a distance of at least 200m - 300m depending on the size of the turbine.
o Designated areas or listed buildings.
National Parks or Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty are more difficult to satisfy the local planning officer to install a wind turbine on it or near it.
Steps to Planning and Building a Wind Farm
There are many stages of development before a wind turbine/farm can be approved and built. Once a site has been selected for its good overall potential, work begins on several main tasks:
- Consultation with the local authority
It is extremely important to contact the local authority in the area where the turbine is considered before committing any time or costs. Engage them early in the planning process, answer any questions and/or concerns that they might have, and keep an open dialogue with them throughout the whole development.
- Consultation with the Public near the site
The local community who are likely to be affected by the proposal must be met to present the project, solicit their feedback and seek their support. An advertisement in the local paper would be a good idea to inform the general public and invite them for a discussion and debate.
- Land acquisition
Early in the process, developers, if not already the owners themselves usually approach landowners to negotiate “option” agreements to use their land. As the project progresses, the developer will seek to convert the options into firm land lease agreements.
- Wind Assessment
Another very important step is assessing the wind resource. Scientists and engineers use meteorological masts to measure wind speed and other climatic conditions for at least one year. This data is then used to estimate how much energy the wind farm will produce. It is often assumed that this has to be carried out before any serious consideration is planned.
- Wind Farm Design
This is important if the project is a wind farm, Wind data is combined with topographical information to design the wind farm. Engineers use this data to model wind flow, turbine performance, sound levels and other parameters to optimize the location of the wind turbines. They also design the access roads, turbine foundations and local electric network, as well as the connection to the electricity grid.
- Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental assessments are conducted to identify any impacts on landscape, plants and wildlife, soil and water, land use or other activities such as aviation and telecommunications. If negative impacts are identified, the design is adjusted to avoid or mitigate them.
- Economic and Financial evaluation
To prove the economic viability of the project in order to raise the funds to build the wind farm. On one hand, there is a need to estimate the cost of turbines and their installation, as well as roads, electrical system, operation and maintenance, etc. On the other hand, there is a need to estimate the income from the energy production of the wind farm over the lifetime of the project. If there is a net profit, the project has a chance to succeed.
- Site Preparation
Build access roads and clear the areas where turbines will be erected; then prepare the foundations; do the excavating, followed by installing the formworks and pouring concrete.
- Construction
The wind turbine parts are manufactured and pre-assembled into the main components at the factory then shipped to the wind farm site where the final assembly will take place. When all components have been received, the assembly can take place. A crane is used to erect the tower and install the nacelle and rotor with its hub and blades. On the ground, the electrical collection network is installed and connected to the grid through the substation.
- Commissioning
Finally, the wind turbine is tested, all components are calibrated on site and verified against the suppliers specifications, before becoming fully operational.
Labels
wind power generatorwind power for homeshome wind powerwind powerwind power generatorswind power factswind power generationresidential wind powerwind power plantwind turbine designwhat is wind powerFarming Principle: Deep Soil Preparation
Looking at GB as a three-legged stool, deep soil preparation is one of the legs. Deep soil preparation builds soil and soil structure by loosening the soil to a depth of 24 inches (60 cm). Ideal soil structure has both pore space for air and water to move freely and soil particles that hold together nicely.
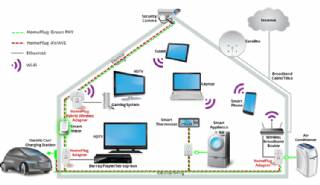
Smart Home Ecosystem - Smart Home Automation - Smart Home Security - Smart Home Technology
The outer-most level corresponds to the individual devices and sensors that consumers interact with. Several candidates are vying for the role of a leader introducing smart home services to the mass market.
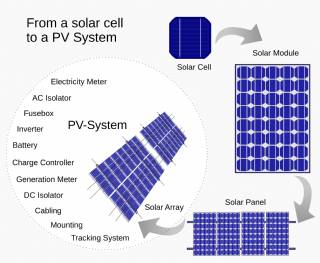
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Modules - Solar Electric System Design - Solar Power
The heart of a photovoltaic system is the solar module. Many photovoltaic cells are wired together by the manufacturer to produce a solar module. When installed at a site, solar modules are wired together in series to form strings. Strings of modules are connected in parallel to form an array.
Solar Energy Systems - Array Mounting Racks - Solar Ray - Solar Panel - PV Racks and Mounts
Arrays are most commonly mounted on roofs or on steel poles set in concrete. In certain applications, they may be mounted at ground level or on building walls. Solar modules can also be mounted to serve as part or all of a shade structure such as a patio cover. On roof-mounted systems, the PV array is typically mounted on fixed racks, parallel to t

Solar Energy Systems - Grounding Equipment
Grounding equipment provides a well-defined, low-resistance path from your system to the ground to protect your system from current surges from lightning strikes or equipment malfunctions. Grounding also stabilizes voltages and provides a common reference point. The grounding harness is usually located on the roof.
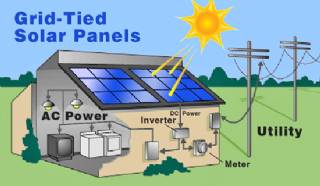
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Inverter - Solar Panel Inverter
Most grid-connected inverters can be installed outdoors, while most off-grid inverters are not weatherproof. There are essentially two types of grid-interactive inverters: those designed for use with batteries and those designed for a system without batteries.
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Disconnects
Automatic and manual safety disconnects protect the wiring and components from power surges and other equipment malfunctions. They also ensure the system can be safely shut down and system components can be removed for maintenance and repair.

Solar Energy Systems - Solar Battery Bank
Batteries store direct current electrical energy for later use. This energy storage comes at a cost, however, since batteries reduce the efficiency and output of the PV system, typically by about 10 percent for lead-acid batteries. Batteries also increase the complexity and cost of the system.
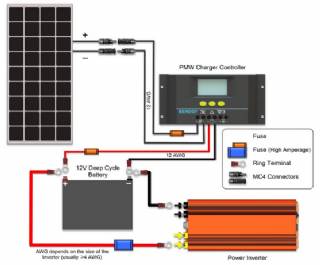
Solar Energy Systems - Solar Charge Controller
A charge controller, sometimes referred to as a photovoltaic controller or battery charger, is only necessary in systems with battery back-up. The primary function of a charge controller is to prevent overcharging of the batteries. Most also include a lowvoltage disconnect that prevents over-discharging batteries. In addition, charge controllers pr
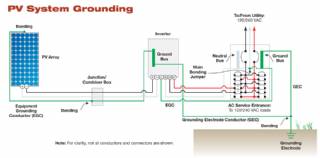
Solar Energy Systems - The NEC and PV Systems
Solar PV systems must be installed in accordance with Article 690 of the National Electric Code, which specifically deals with PV systems, as well as several other articles of the NEC that pertain to electrical systems in general. When there is a conflict between NEC 690 and any other article, NEC 690 takes precedence due to the unique nature of PV